A Case for Launching Your Own AI Quality Companion
05/12/2025

Explore how TAUS EPIC API's Quality Estimation can revolutionize translation workflows, that offer scalable, domain-specific solutions for Language Service Providers without the need for in-house NLP experts.
Author

Jaap van der Meer founded TAUS in 2004. He is a language industry pioneer and visionary, who started his first translation company, INK, in The Netherlands in 1980. Jaap is a regular speaker at conferences and author of many articles about technologies, translation and globalization trends.
Related Articles
 by David Koot
by David Koot09/01/2026
TAUS EPIC API's customizable Quality Estimation models can enhance translation workflows and meet specific needs without requiring in-house NLP expertise.
30/10/2025
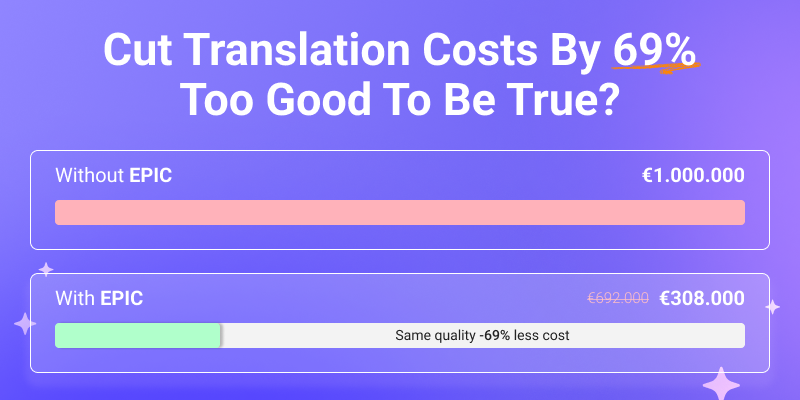
See your translation ROI with Quality Estimation (QE) and Automatic Post-Editing (APE). Find out how EPIC can reduce post-editing costs by up to 70% while improving efficiency.
28/08/2025
LLMs' limitations on QE tasks versus more specific solutions like TAUS EPIC